CÁC THÀNH TỰU CHÍNH
.PNG)
Department Head
Assoc.Prof. Do Manh Hung
|
MISSION:
-
Carry out basic research, training and educating post-graduate students in magnetism and magnetic materials.
MAIN RESEARCH DIRECTION:
-
Fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles, study of structure, magnetic properties and applicability in biomedicine
-
Multilayer magnetic films and applications
-
Metamaterials and Applications
-
Simulation of metal atom cluster properties
|
 manhdh@ims.vast.ac.vn manhdh@ims.vast.ac.vn |
 +84 904 233 353 +84 904 233 353 |
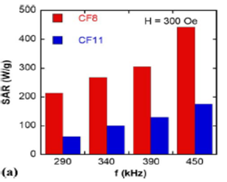
Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles (CFO NPs) were synthesized using thermal decomposition of organometallic precursors to develop a superparamagnetic nanosystem with enhanced specific absorption rate (SAR) for advanced magnetic hyperthermia therapy (MHT). The results show that CFO NPs have spherical shape, average particle size 8-11 nm, narrow size distribution, and high saturation magnetization (70 emu/g). Large SAR values of the CFO NPs are achieved, which are superior to those reported previously in the literature. The high heating efficiencies of the present CFO NPs make them a promising candidate for advanced MHT (see: D. H. Manh et al, Adv. Nat. Sci.: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11 (2020) 045005, https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6254/abbc68 for more details).
 |
(b)
|
Fig. 1. (a) SAR as a function of (a) the magnetic field frequency for a fixed field amplitude of 300 Oe for the CF8 (8 nm) and CF11 (11 nm) samples. (b) a typical SEM image of CF8.
Fe/Fe3O4 nanocomposites are synthesized by combined high energy ball milling and controlled oxidation under (oxygen and nitrogen) gas flow. An X-ray diffraction analysis of the crystal structure of the nanocomposites confirmed the coexistence of Fe and Fe3O4 phases and an increase of the oxygen concentration during oxidation process led to the formation of a higher fraction of the Fe3O4 phase with good crystallinity and stoichiometry.
Hình 2. Nanocomposite Fe/Fe3O4 tiêu biểu (được xử lý nhiệt trong môi trường chứa 30% khi O2: (a) Ảnh TEM được ghi nhận trên kính hiển vi điện tử quét Hitachi S-4800. (b) Hiệu ứng Vervey được quan sát từ đường cong từ độ phụ thuộc nhiệt độ M(T) trong kiểu làm lạnh không đặt từ trường
The morphology of the nanocomposites revealed a lamella-like structure with a thickness of about 30 nm. Interestingly, the lamellae exhibited a sharp Verwey transition near 120 K, which is often suppressed or absent in nanostructured Fe3O4 due to the poorly crystalline, off-stoichiometric characteristic. Our study demonstrates the possibility of tuning the magnetism in iron/iron oxide nanosystems through controlled oxidation. (see: H.M. Do et al, Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices 5 (2020) 263-269, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2020.04.001 for more details).
-
Binary clusters of transition-metal and noble-metal elements have been gathering momentum for not only advanced fundamental understanding but also potential as elementary blocks of novel nanostructured materials. In this regard, the geometries, electronic structures, stability, and magnetic properties of Cr-doped Cun, Agn, and Aun clusters (n = 2−20) have been systematically studied by means of density functional theory calculations. It is found that the structural evolutions of CrCun and CrAgn clusters are identical. The icosahedral CrCu12 and CrAg12 are crucial sizes for doped copper and silver species. Small CrAun clusters prefer the planar geometries, while the larger ones appear as on the way to establish the tetrahedral CrAu19. (see: (chi tiết: Mai et al, ACS Omega 2021, 6, 20341−20350, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c02282 for more details).
-
A metamaterial (MM), mimicking electromagnetically-induced transparency (EIT) in the GHz regime, was demonstrated numerically and experimentally by exploiting the near-field coupling of asymmetric split-ring and cut-wire resonators. By moving the resonators towards each other, the original resonance dip was transformed to a multi-band EIT. The phenomenon was explained clearly through the excitation of bright and dark modes. The dispersion characteristic of the proposed MM was also investigated, which showed a strongly-dispersive behavior, leading to a high group index and a time delay of the MM. Our work is expected to contribute a simple way to develop the potential devices based on the multi-band EIT effect.
-
Hung Manh Do, et al, Oxidation-controlled magnetism and Verwey transition in Fe/Fe3O4 lamellae, Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices 5 (2020) 263-269.
-
Do Hung Manh, et al, High heating efficiency of interactive cobalt ferrite nanoparticle, Adv. Nat. Sci.: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11 (2020) 045005.
-
V.H. KY et al, Experimental Study and Monte-Carlo Simulation of Exchange Bias Effect in Co-CoO Composite Powder Fabricated by High-Energy Ball Milling, Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS 48 (2019) 7952–7959.
-
T.N. Bach, et al, Microwave absorption properties of (100_x)La1.5Sr0.5NiO4/xNiFe2O4 nanocomposites, Journal of Alloys and Compounds 695 (2017) 1658-1662.
-
Ngo Thi Hong Le, et al, Photocatalytic and water-splitting properties of TiO2 and Ag–TiO2 films in the visible light region, AIP Advances 11 (2021) 075118, doi: 10.1063/5.0058116.
-
T.N. Anh Nguyen et al, Effect of flattened surface morphology of anodized aluminum oxide templates on the magnetic properties of nanoporous Co/Pt and Co/Pd thin multilayered films, Applied Surface Science 427 (2018) 649–655.
-
Pham Hoai Linh et al, A Facile Ultrasound Assisted Synthesis of Dextran-Stabilized Co0.2Fe0.8Fe2O4 Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Application, IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS 54 (2018) 5400204.
-
Nguyen Thi Mai et al, Systematic Investigation of the Structure, Stability, and Spin Magnetic Moment of CrMn Clusters (M = Cu, Ag, Au, and n = 2−20), ACS Omega 2021, 6, 20341−20350.
-
Tung B.S., et al, Multi-Band Electromagnetically-Induced-Transparency Metamaterial Based on the Near-Field Coupling of Asymmetric Split-Ring and Cut-Wire Resonators in the GHz Regime, Crystals 11 (2021) 164.
-
Xuan Khuyen Bui, et al, Simple design of efficient broadband multifunctional polarization converter for X‑band applications, Scientific Reports 11 (2021) 2032.
-
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM)
Characterization of field and temperature dependence of magnetization of powder or bulk magnetic materials, M(H) and H(T) with the highest magnetic field 11 kOe in the temperature range from 177K to 500K.
-
Physical properties measurement system – VersaLab
Characterization of magnetic properties and electrical conductivity of powder, thin film, bulk materials. Temperature: 50K - 400K, the highest magnetic field is 3 Tesla.
-
High energy ball mill: SPEX 8000D and Fritsch Pulverisette 6.
-
Dry grinding: It is possible to reduce the size of oxide powder, metallic materials (hard, brittle) to about 10 nm (minimum) for dry grinding and a few micrometers in size for wet grinding.
-
Low frequency noise measurement system under 100 MHz
-
Some equipment and tools for synthesizing materials by chemical methods (co-precipitation, hydrothermal) and heat treatment: furnace (1100oC), vacuum drying oven (300oC).